
Want to know how you can increase your testosterone levels? Healthy hormones will forever work in your favor, after all.
T plays a pivotal part in many vital health markers, influencing everything from brain power, to muscle mass and even heart health.
It’s safe to say testosterone is the most important hormone in a man’s body and high on the list for women, so optimizing it makes sense.
The benefits of increasing yours could cause dramatic life improvements – if there’s enough headroom for the hormone.
What is testosterone?
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone with an expansive spectrum of roles in the body.
It’s best known for triggering the development of masculine traits and maintaining them in men as they age. Women produce need testosterone too, but in tiny amounts, hence their naturally low levels.
Saying testosterone turns boys into men isn’t anything you didn’t know already.
However, there’s more to the potent androgen hormone than meets the eye. Almost every aspect of your life (if you’re a man) is touched by T, some things you’d never even think of.
Functions of testosterone include and influence:
- Muscle growth, maintenance, and strength
- Bone density
- Cardiovascular health
- Mood – mental wellbeing
- Sexual health and performance
- Energy – metabolism & red blood cell production
- Behavior – assertiveness, competitiveness, & aggression
It’s not only when you’re a fully grown adult that testosterone has a say in life. If you’re reading this as a male, T might have started triggering changes as early as seven weeks after conception.
Read more about what testosterone is in our complete guide.
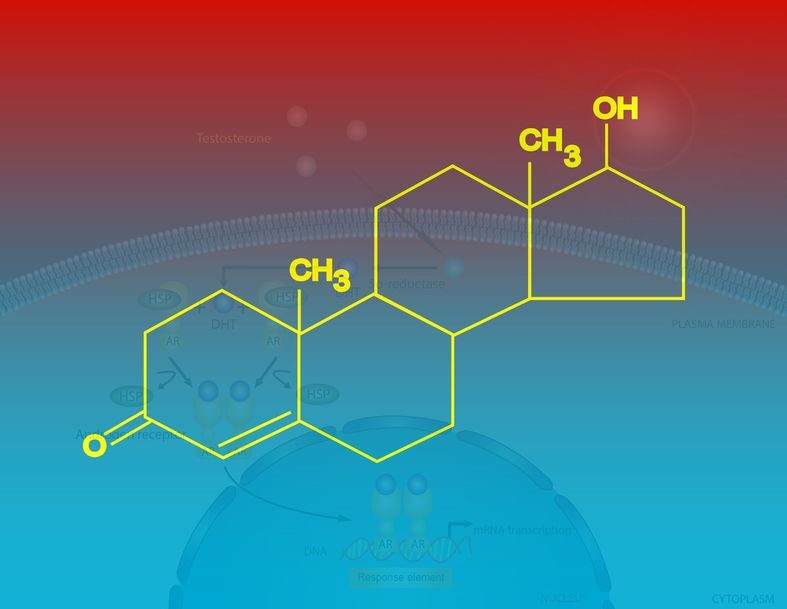
Low testosterone levels in men
Testosterone production can amplify around thirty times throughout adolescence. It ramps up toward puberty before hitting a peak at age 19, starting a slow decline at about age 30.
A lot of men live their entire life with no abnormalities to their testosterone. Age-related androgen loss is normal and expected too. It’s not something doctors worry about too much, even if we do.
Unfortunately, though, lower testosterone or hypogonadism can be a life shaking issue for some people.
Hypogonadism is the medical term for low testosterone levels below 300 ng.dL, whereas lower levels might just sit at the bottom end of the normality scale.
Any man can experience low testosterone at any age – it’s important to spot the symptoms early and take a blood test if you do.
Low testosterone’s side-effects can cause severe health complications if left untreated, some may be irreversible.
Depending on the severity of your low T, you might just be prompted to make simple, but effective lifestyle adjustments.
After all, testosterone is extremely sensitive to its environment, responding well and possibly thriving alongside a healthy diet, exercise, and sleep routine.
However, if your doctor feels medical intervention will be better, you might be offered testosterone replacement therapy – aka TRT.
Symptoms of low testosterone include:
- Muscular atrophy
- Low libido, decreased sexual performance, & infertility
- Frailty
- Bone loss
- Low mood – irritability, anxiety, & depressive thoughts
- Weight gain
- Reduced cognitive function
- Sleep problems
- Increased risk of obesity
- Increased risk of heart disease
- Accelerated risk of diabetes
- Increased risk of metabolic syndrome
- Heightened mortality risk
Step in early to stop the side effects of low testosterone taking control.
What are the benefits of increasing testosterone levels?

Increasing testosterone can actively help to reverse the symptoms of deficiency.
After all, reinvigorating production or replenishing levels can fill the void left open, providing the very substance needed to attach to androgen receptor sites.
Why is this important? Because T binding to a receptor is like hitting a button that triggers important functions.
Androgen receptors are literally waiting to be signaled, so they can instruct for things to happen.
1. Better body composition
Body composition is the ratio of muscle to fat strapped to your frame.
Many men with previously low T report noticing an increase in muscle mass after starting TRT.
Studies have also shown that the simple act of raising testosterone alone can be enough to promote fat loss. Combine the two and you have a strong body with a healthy, lean composition[1].
It’s estimated that obese men typically have 30% lower testosterone than other guys of a healthy weight[2]. Excess fat, especially the visceral belly kind, works to lower testosterone and may even cause the conversion of testosterone into estrogen[3].
By achieving and maintaining a healthy body composition, you steer clear of the T-dampening trap caused by being overweight.
Improving testosterone can help minimize your risk of complications in the first place and lower your chances of developing serious disease.
2. Muscle growth
If there’s one thing testosterone is notorious for driving, it’s muscle growth.
Testosterone has a direct part in instigating muscle protein synthesis (MPS), which is the process of building lean muscle mass.
If testosterone diminishes, so does your ability to stack thick, strong muscle[4]. One of the first noticeable signs of testosterone deficiency is muscular atrophy, often accompanied by weakness.
Weight training can help to maximize any muscle growth instigated by increased testosterone.
Muscle fibers react to the stimulus provided, and thanks to T stimulated MPS, should grow as a result. Studies show that resistance training is not only the primary driver of muscle gains[5], but can also boost testosterone too[6].
Plus, the more muscle you have, the more that can be activated during training, potentially instigating a larger testosterone release.
3. Boosted brain power
Research suggests there’s a clear connection between cognitive ability and testosterone status[7].
Healthy hormones can keep you sharper and improve memory, whereas deficiencies cause the opposite effect.
It’s not just a coincidence that cognitive performance and testosterone both decline with age.
Increasing T may boost brain power when cognitive dysfunction is linked to low testosterone[8][9].
4. Sex drive and performance
Sexual health in both sexes relies heavily on testosterone. Libido can be one of the first things to disappear when T suffers, which can often be accompanied by erectile issues and low sperm quality.
You may discover your sex drive disappears completely, or even if you feel like having intercourse, you physically can’t. Understandably, these scenarios can have a substantially negative impact on your mental wellbeing.
Because of how intrinsic sex and testosterone is, replenishing levels back to normal may help reverse low-libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility[10]. However, low testosterone isn’t always the cause of ED.
Visit your doctor to discuss erectile dysfunction if issues arise.
5. Energy
Fatigue is a common complaint for men with low testosterone men. Interestingly though, scientists aren’t exactly sure why increasing T helps rejuvenate energy supplies.
They speculate things might be down to T’s influence on mitochondria, the power station inside your cells. It is thought testosterone could flick their switch and make them more active.
Alternatively, some experts suggest fatigue might be caused by unstimulated androgen receptors. While no-one is really sure what’s happening, the energizing effects of boosting T is still a major benefit.
6. Stronger bones
Strong bones are an integral part of any healthy body. They provide an anchor and support for muscles, protect vital organs like the heart, and reduce the risk of fractures.
Testosterone works to promote bone mineral density, which makes bone loss a dangerous side effect of low testosterone.
Studies show that restoring testosterone in hypogonadal men help to improve lost bone strength[11].
Doing so should also reduce the risk of skeletal injury and fractures.
7. Better mood
Low testosterone can quickly start to impact your mental wellbeing. Hypogonadal men have been known to experience anxiety, irritability, and depression as a side effect of their condition[12].
All in all, lower T can cause a downturn in overall quality of life.
Reverse hypogonadism by replacing testosterone, however, and it appears your mood might increase too.
When therapists helped hypogonadal men raise their deficient hormones, they saw an improvement in depressive symptoms[13].
There’s also a touch of evidence showing how increasing testosterone may be an effective treatment for supporting the mental wellbeing of certain men.
It’s believed TRT could help improve their status of the ‘happy hormone’ serotonin.
It’s important to understand how these results were seen in cases of clinically diagnosed hypogonadism. Age-related testosterone decline might not necessarily make you anxious or depressed.
TRT and its risks
Testosterone replacement therapy – aka TRT – is used by millions of Americans today.
It’s typically used to treat clinical hypogonadism, but many clinics still market TRT as an answer to aging in men.
Patches, creams, gels, and most notoriously, injections, are prescribed to boost levels of the masculine hormone in the hope to reverse the symptoms of low testosterone.
But, for all the wonders TRT promises, it isn’t safe from scrutiny. Many professionals still air their concerns about the risks involved and long-term health effects aren’t known.
No one currently knows what issues TRT users might face in later life.
Testosterone replacement therapy is exactly what its name suggests.
A synthetic, lab-created version of testosterone is administered to your body, replacing the need for natural production, and hiking up your T levels instantly.
Taking TRT can help rejuvenate your levels and bring them back up to a healthy amount.
As we mentioned though, the long-term impacts of taking TRT aren’t yet known. Adverse side-effects currently recognized include:
- Prostate enlargement
- Breast enlargement
- Oily skin & acne
- Infertility
- Aggravation of sleep issues such as sleep apnea & insomnia
What are the alternatives?
TRT isn’t the only option for increasing testosterone levels. You may be reading this with lower T caused by lifestyle issues, or as a staple side-effect of aging.
For some men, both the known and unknown risks of TRT just don’t sit well with them. Fortunately, there are alternatives.
Your doctor may advise you to adjust your lifestyle if it’s impacting your testosterone. It’s not uncommon for obese men with lower T to be encouraged to lose weight, for example.
Alternatively, if you’re lacking certain nutrients, a dietician might help fix your food choices to promote T production.
Testosterone creation isn’t just a simple, single on-off switch. There are many independent cogs spinning in the T machine, which can cause disruptions in production if one or more break.
A healthy well-nourished body is the perfect environment for testosterone to thrive, which is why you should start here.
How to increase your testosterone levels naturally
Naturally increasing testosterone doesn’t need to be complicated.
Like we just mentioned, it all begins with creating a tranquil, optimized, and well-balanced body.
You can start by re-building the four pillars that uphold all health; diet, exercise, sleep, and stress.

1. Diet
They say you are what you eat – especially when it comes to testosterone. First of all, T is synthesized from cholesterol, which makes eating enough healthy fats paramount.
Studies show that a low-fat diet can have a detrimental impact on testosterone production in men, which goes against what a lot of mainstream dieting advice says. Stick to the healthy, natural fats.
Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D are three other nutrients whose status affects testosterone.
Deficiencies can cause distinct drops in production, yet, evidence suggests replenishing stores can reverse the effect. Make sure to fill your diet with all three by eating the right wholefoods or employing a supplement.
Speaking of supplements, Ashwagandha and D-Aspartic Acid both appear to offer improvements in testosterone production and fertility.
While Ashwagandha has reported benefits for all kind of men, D-AA is shown to be more beneficial for people with pre-existing lower testosterone levels.
Both Ashwagandha and D-AA can be found as standalone supplements or as part of more expansive testosterone boosters.
2. Exercise
Men who exercise typically have higher testosterone than sedentary, sit-around all day types[14][15], and being active could help obese men improve their T count more than weight loss alone[16].
Weightlifting appears to offer the most benefit[17][18][19], followed by HIIT[20][21], then moderate cardio.
Try to steer clear of chronic endurance training and any super-long sessions[22]. Exercising for too long can have an opposite, T-reducing effect.
3. Sleep
Studies show that sleep deprivation can severely sever next day testosterone.
According to one piece of research from 2011, the effects of only resting five hours could change testosterone as much as 10-15 years of natural aging[23].
Aim to sleep for a minimum of seven or eight quality hours every single night for healthier T.
4. Stress
Stress releases a hormone of its own called cortisol.
Although this can prove to be a positive occurrence in the short-term, extended, otherwise known as chronic stress can become an issue.
It’s seriously harmful to health, having a hand in the increase in modern all-cause mortality, and can quickly cut ties with healthy testosterone levels[24][25][26][27].
If you want to improve your T, take quick action against stress and make more time to relax.
Exercise can be a great way to unwind, as well as picking up a calming hobby, spending more time outdoors, and practicing mindfulness.
The Final Word
Increasing testosterone levels can reinvigorate your energy levels and ability to maintain a lean, strong and healthy body.
Your mental wellbeing can experience a lift too, enhancing your overall experience of life. However, taking TRT isn’t without the risks, and most of the dramatic benefits are seen in men with clinically diagnosed hypogonadism.
If your testosterone levels aren’t significantly low, you might not see the same results, or even be offered therapy.
There are ways to naturally improve and increase testosterone levels. It all starts with a healthy body and mind, which are two things you can have a hand in.
Create the best environment for healthy hormones by respecting your body every day. TRT isn’t always the only answer.
References
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701485/
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20173018
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12198740
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2917954
[5] https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.1990.12.6.248
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17051372
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17132744
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27545990
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5209560/
[10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701485/
[11] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701485/
[12] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701485/
[13] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2701485/
[14] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22234399
[15] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15204068
[16] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4706091/
[17] https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00423247
[18] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3040039/
[19] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17051372
[20] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23310924
[21] https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/25373470
[22] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5988228/
[23] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4445839/
[24] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6348068/
[25] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3880087/
[26] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3341916/
[27] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29884468




Leave a comment